PERITONEAL DIALYSIS
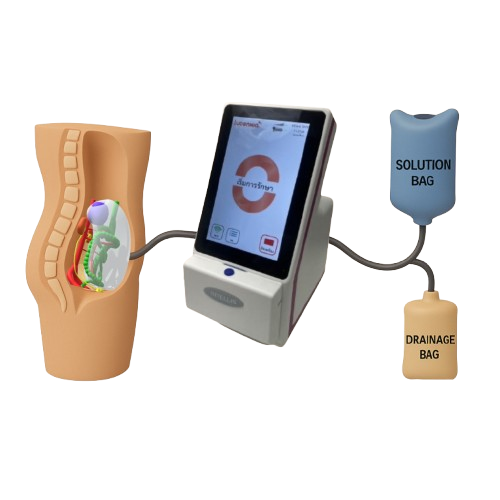
Peritoneal Dialysis (PD) is a gentle, home-based treatment for kidney failure that uses the body's natural lining inside the abdomen to filter waste and excess fluids from the blood. A cleansing fluid is introduced into the abdomen through a soft tube and later drained, helping patients maintain their daily routines with greater freedom and flexibility.